- Docker On Elementary Os
- Docker Elementary Os Hera
- Install Docker Elementary Os Hera
- Docker For Elementary Os
- Elementary Os Install Docker
A word of warning: There are a lot of unofficial packages and repository sources around. These are build by third parties and may contain malicious code! Please make sure to use only the sources mentioned here to install albert.
Details for docker License Apache-2.0 AND GPL-2.0 AND MIT Last updated 12 February 2021 Share this snap. Generate an embeddable card to be shared on external websites. Ubuntu is built on Debian's architecture and infrastructure, and comprises Linux server, desktop and discontinued phone and tablet operating system versions. Ubuntu releases updated versions predictably every six months, and each release receives free support for nine months (eighteen months prior to 13.04) with security fixes, high-impact bug fixes and conservative, substantially beneficial. By analyzing a Docker image, we can discover possible duplicate files across the layers and remove them to reduce the size of the docker image. The Dive utility is not just a Docker Image analyzer, but also helps us to build one. Dive is free, open source tool written in Go programming language. Installing Dive. In Open source world there are couple of free email server but Zimbra is one of the. Next Elementary OS 5.0. How to Install and Use Docker on Ubuntu 20.04 / 20.
Using a package manager is highly recommended, since it is less error prone and the necessary dependencies are pulled automatically.
Using official albert repositories

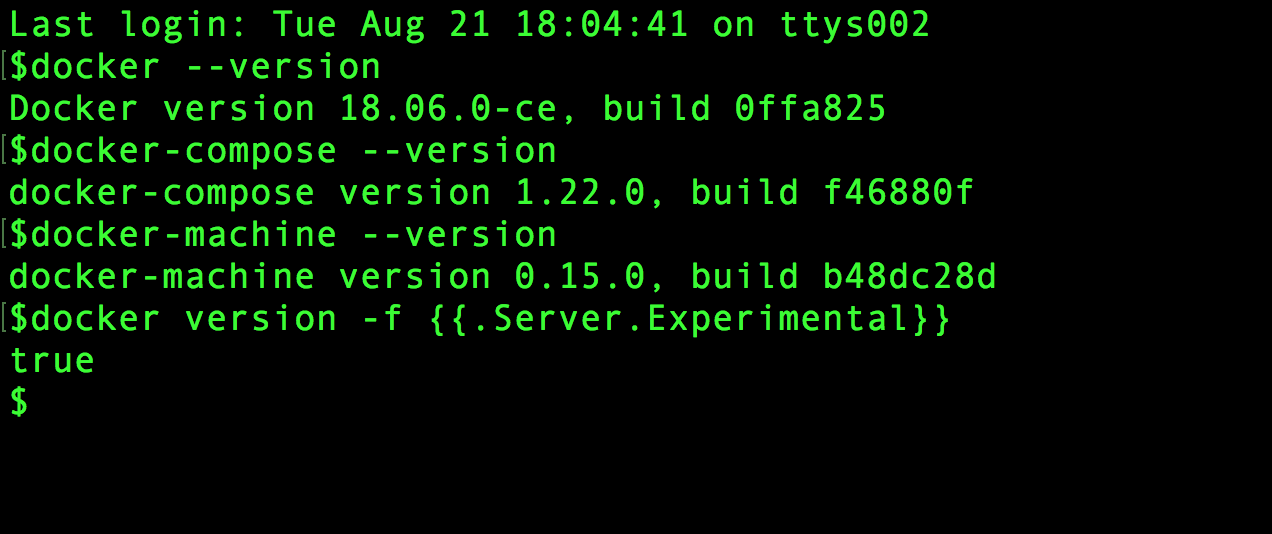
Docker On Elementary Os
For all other distros or simply if you want to receive updates as soon as they are pushed on github, you can use the prebuilt binaries hosted at Open Build Service. OBS is a platform designed to compile packages for multiple Linux distributions and simplifies the packaging process, so developers can more easily package a single program for many distributions. Whenever GitHub receives a tag, a webhook starts the compilation, packaging and publishing for several distributions on OBS. Finally the Albert package is public in the repos of OBS, and can be pulled by package managers.
Before you can use this repo you have to add a keyfile to your package manager, which is used to verify the integrity of the packages it later receives. For details see debian.org and redhat.com. Keep in mind that the key has an expiration date and you have to repeat this process every few years. Depending on your package manager this step varies.
For RPM based package managers:
For DEB based package managers:
To tell your package manager to use the OBS repo, you have to give it a link to the correct repo matching your distribution. Note that, if you are using derived distributions, you have to use the distribution, which your OS is based on. I.e., using Linux Mint 20, you have to use the xUbuntu_20.04 repository, since Linux Mint 20 is based on Ubuntu 20.04.
Docker Elementary Os Hera
To find the link of the distribution you need visit the OBS software repo and follow the instructions there. There you will find the remaining steps you have to run in your terminal to add the repo and install albert. If there are some popular distributions or recent versions of them missing, leave a note in the community chat.
These steps have to be done only once. From now on Albert will be updated like any other package on your system.
Using official albert packages
This is an option if you just want to test Albert or if you do not want to get rolling updates, but rather stay with a particular version instead. For all other cases use the methods above. You will find the precompiled packages here.
From source
This way is usually for developers only. Building from sources is the least convenient, but most flexible way. The build process is trivial, but you have to manage the dependencies on your own. Before you can start building Albert you need some libraries.
Prerequisites
The goal is to be always compatible with the latest Ubuntu LTS release. To build Albert from sources you will need CMake, a C++ compiler supporting at least the C++14 standard, and the Qt toolkit.
Further the plugins may introduce optional dependencies, e.g the calculator plugin needs the muparser library and the QMLBoxModel frontend needs the QtDeclarative library. Check the docker files for an up to date list of dependencies.
Problems may arise with distributions that split submodules into optional dependencies. Ubuntu is known to split the SQL driver submodules into separate packages. Additionally, Elementary OS - which builds on Ubuntu - does not install optional dependencies. Users may therefore encounter linkage errors and have to explicitly install the missing dependencies.
Install Docker Elementary Os Hera
Another concern is the difference between compile time and runtime dependencies. Some distributions ship libraries as single packages while others ship a normal package and a *-dev package. Dev packages usually contain the header files and static libraries in addition to the shared libraries. Normal packages are stripped down to the shared libraries. On distributions that do not differentiate between these kinds of packages, basically every package is a dev package. For the compilation on e.g. Ubuntu, dev packages are needed at compile time but at runtime normal packages are sufficient. If the optional dependency of a plugin is not available at runtime it will refuse to load; the core application will run fine though.
Compilation
To configure, build and install run the following commands:
Lets go through them and clarify what they do. The first command clones the Albert git repository to the local file system. Since no destination directory is specified a directory with the name of the repository is created. The next step is to create the out-of-source-build directory. A self-explanatory name is always a good one.
Docker For Elementary Os
After changing the working directory to the just created build directory the cmake command configures the build environment and creates the makefiles. The first positional parameter is the path to the source directory which contains a file called CMakeLists.txt. The -D parameter sets CMake variables.
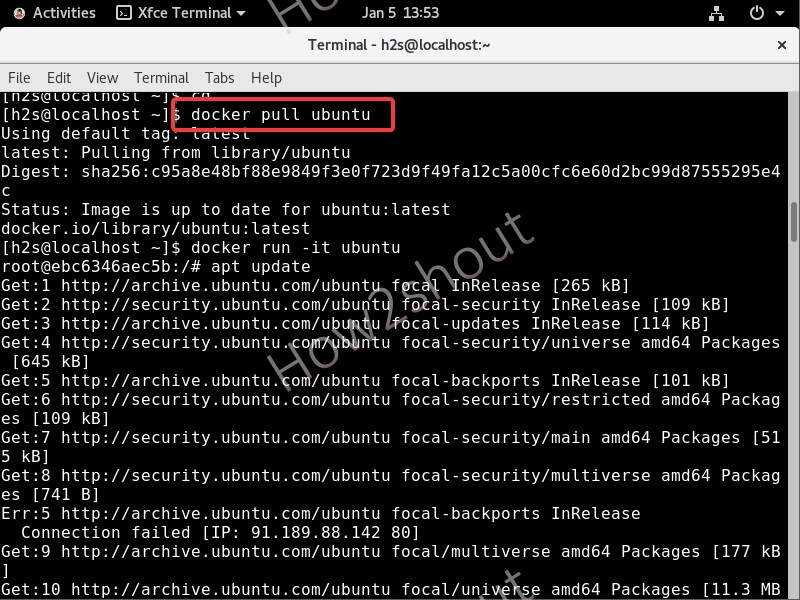
The CMake variable CMAKE_BUILD_TYPE specifies the build type to use. If you want to report bugs it makes sense to build a Debug build, since the build then produces debugging information with which GDB can work. Core dumps of this build can be used to track down issues. Futher the make output is more verbose. If you dont want any of those that use the build type Release.
CMAKE_INSTALL_PREFIX defines the prefix for the installation directory. This value usually defaults to /usr/local. Since albert looks up libraries, plugins and stylefiles etc only /usr, /usr/local are supported. If you still want to make it work somewhere else, you have to use environment variables to manipulate XDG base dir specs and the lookup paths of the dynamic linker. Do absolutely not do this unless you exactly know what you are doing.
Elementary Os Install Docker
Finally make builds the application and sudo make install installs the application on your system. Albert is not a portable application so the install step is mandatory.
